


Next: 3.1.4.4 Confidentiality and integrity
Up: 3.1.4 Provision of security
Previous: 3.1.4.2 Key management
Access
control
rules
(typically
for
an
administratively-imposed
policy
category)
can
be
enforced
centrally
from
the
security
management
console.
Access
to
resources
can
be
granted
on
a
need-to-know
basis
based
on
the
workgroup
a
subject
is
a
member
off
(i.e. an
identity-based
policy
class).
When
the
subject
changes
to
a
different
workgroup,
his
access
rights
are
automatically
updated.
Attempts
to
access
restricted
resources
are
monitored
and
logged.
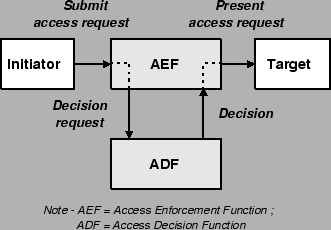
In
ISO
10181-3
speak,
an
initiator
would
submit
an
access
request
to
the
access
control
enforcement
function
(AEF)
which
ensures
that
only
allowable
accesses,
as
defined
by
the
access
control
decision
function
(ADF)
are
performed
by
the
initiator
on
the
target
[ISO94].
Figure 3.4:
The
ISO
access
control
model
|
According
to
our
model,
the
AEF
would
be
an
integrated
monitor
and
decision
enforcement
application.
The
AEF
sends
its
initiator
and
target
access
control
decision
information
(ADI
-
all
or
part
of
the
information
the
ADF
needs
to
make
an
access
control
decision,
typically
expressed
in
capability,
label-based,
access
control
list
or
context-based
schemes)
to
the
ADF
through
the
AS-API.
The
ADF
checks
with
the
security
management
service
for
access
control
policy
rules
and
now
has
the
information
to
make
a
decision.
The
decision
is
sent
back
to
the
AEF
(the
decision
enforcement
function)
through
the
AS-API.



Next: 3.1.4.4 Confidentiality and integrity
Up: 3.1.4 Provision of security
Previous: 3.1.4.2 Key management
(c) 1998, Filip Schepers
